Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the quiet engine behind the “how did it know what I meant?” moments on modern websites. We have watched a WooCommerce store owner copy-paste 200 support emails into a spreadsheet at 11:47 PM and we have also watched that same workload drop to a tidy review queue the next week.
Quick answer: NLP turns messy human text (emails, chats, reviews, form entries) into structured signals your site and team can act on, as long as you add guardrails for accuracy and privacy.
Key Takeaways
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) turns messy text from emails, chats, reviews, and forms into structured signals your team can route, measure, and act on.
- Treat NLP like a fast junior assistant—use it to classify, extract, summarize, and draft, but add checks because models can be confidently wrong.
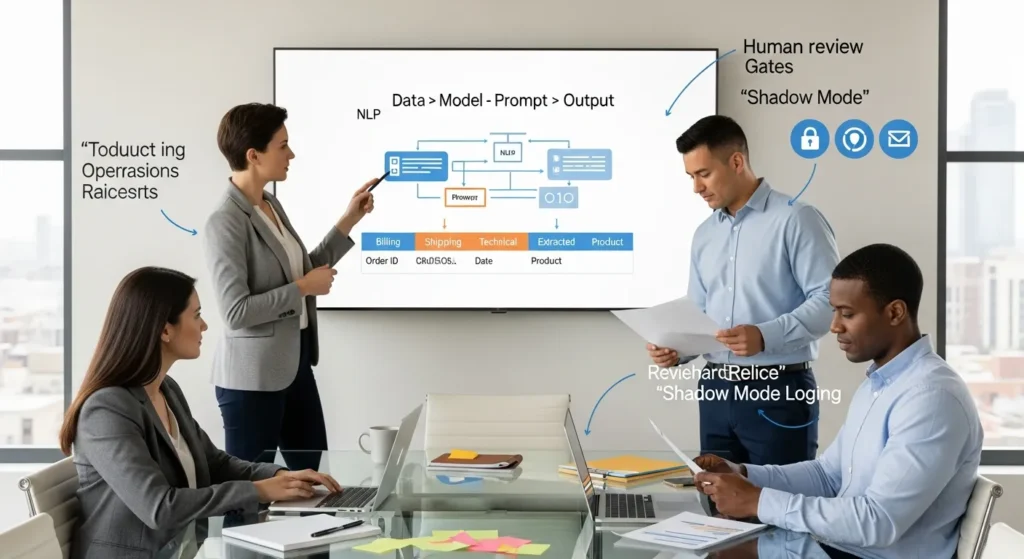
- Improve output quality by mapping the AI stack (data → model → prompt → output) and choosing the smallest, safest task first, especially classification and extraction.
- Use a reusable workflow map (trigger/input/job/output/guardrails) and start in shadow mode with logging and human review gates before enabling any customer-facing actions.
- Implement NLP in WordPress with webhooks, automation tools, hooks, custom fields, and queues so jobs run reliably without slowing page loads or publishing errors.
- Reduce risk with data minimization, redaction, retention limits, and regulated-content review processes, then pilot one text-heavy queue with one metric and a clear rollback plan.
What NLP Is (And What It Is Not)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) lets software read and work with human language. NLP helps a system detect intent, pull key details, and draft responses. IBM describes it as a field that helps computers understand and process human language, in text or speech.
NLP is not “the computer understands like a human.” Models guess based on patterns in data. That guess can be useful, but it still needs checks. We treat NLP like a junior assistant that is fast, tireless, and sometimes confidently wrong.
Where NLP Sits In The AI Stack: Data → Model → Prompt → Output
Here is the simple chain we map before we touch any tools:
- Data affects model behavior. If your training or reference data is messy, outputs get messy.
- Model affects output quality. A small classifier can be great for routing tickets. A large language model can draft text, but it can drift.
- Prompt affects output format. A clear prompt forces consistent structure. A vague prompt invites surprises.
- Output affects downstream actions. If you auto-publish, you accept higher risk. If you save drafts for review, you cut risk.
On WordPress, this matters because one bad output can publish a wrong claim, email a customer the wrong refund policy, or tag a lead incorrectly.
Common NLP Tasks: Classify, Extract, Summarize, Generate
Most business wins come from four tasks:
- Classification: Your help desk triage goes from one big inbox to clean buckets like “billing,” “shipping,” and “technical.”
- Extraction: The system pulls order IDs, dates, product names, and locations from text.
- Summarization: Long email threads become a short brief for a human agent.
- Generation: The model drafts product descriptions or reply suggestions.
We like to start with classify and extract. They usually give the fastest payoff with the lowest risk.
How NLP Works At A High Level
NLP pipelines convert words into numbers, then numbers into predictions. Google’s Machine Learning Crash Course explains that models need numeric features, so text must become a numeric representation before a model can learn patterns.
A practical way to think about it: text is raw material, the model is the brain, and your workflow is the hands and feet.
Tokens, Embeddings, And Context Windows In Plain English
- Tokens are chunks of text. A token can be a word, part of a word, or punctuation.
- Embeddings map tokens into vectors (lists of numbers). Similar meanings often land near each other in that vector space.
- Context windows set how much surrounding text the model considers at once.
Context affects meaning. “Charge” in “charge my card” differs from “battery charge.” A wider context window helps the model pick the right meaning.
Rules-Based, Machine Learning, And LLM Approaches
You usually pick one of three approaches:
- Rules-based NLP: You write patterns like “if the email contains ‘refund’ then tag as billing.” It is predictable. It breaks when users write creatively.
- Machine learning NLP: A trained classifier learns patterns from labeled examples. It handles variation better.
- LLM-based NLP: A large language model can summarize, extract, and draft in one step. It also needs more guardrails.
Entity choice affects risk. A rules engine affects only what you coded. An LLM affects tone, facts, and formatting unless you constrain it.
Practical NLP Use Cases For Websites And Operations
NLP shines when your business runs on text. Websites create a lot of text: contact forms, reviews, chats, support tickets, product catalogs, blog drafts, and CRM notes.
On-Site Content Workflows: Briefs, Metadata, Internal Linking Suggestions
We often use NLP to speed up content ops without auto-publishing:
- Brief extraction: Turn a founder’s messy voice memo transcript into a structured outline.
- Metadata drafts: Generate SEO titles and meta descriptions as drafts for an editor.
- Internal linking suggestions: Scan a post and suggest 3–6 relevant existing pages to link.
For WordPress teams, this pairs well with a “draft-only” rule. The model suggests. A human approves.
If you want related reading on the site side, pair this with a solid foundation like our guide to WordPress SEO services and your internal linking work starts compounding.
Customer Support And Sales: Triage, Routing, Response Drafts
Support queues are a perfect NLP target:
- NLP classification affects ticket routing. Routing affects response time.
- NLP extraction affects CRM fields. Clean fields affect reporting and follow-up.
- NLP drafting affects first replies. First replies affect customer mood.
A common setup: classify and summarize every new ticket, then post a short brief into your help desk. Agents reply from the brief, not from scratch.
Commerce And Forms: Product Enrichment, Lead Qualification, Intent Detection
Ecommerce and lead gen sites create two constant problems: thin product data and messy form entries.
NLP can help by:
- Enriching product attributes from supplier descriptions (materials, dimensions, compatible models).
- Detecting intent in contact forms (“need a quote” vs “need support” vs “press inquiry”).
- Qualifying leads by pulling budget ranges, timelines, and location.
We see strong results when the output goes into custom fields, not into public copy. That keeps the workflow safe and measurable.
If your store runs on WooCommerce, this also connects to your broader site build work. A clean data model makes WooCommerce solutions easier to scale.
A Simple NLP Workflow Pattern You Can Reuse
We use one pattern again and again because it keeps projects sane.
Trigger / Input / Job / Output / Guardrails
Start every build with this map:
- Trigger: New form submission, new help desk ticket, new WooCommerce product, new review.
- Input: The smallest text you need. Keep it short. Keep it clean.
- Job: Classify, extract, summarize, or draft.
- Output: Tags, fields, a summary note, a draft reply, a status change.
- Guardrails: Validation rules, banned topics, human review steps, and logging.
This pattern prevents the “we connected an API and now we are scared to touch it” problem.
Shadow Mode, Logging, And Human Review Gates
Shadow mode means the model runs, but it does not change customer-facing systems. It only writes to a log or a private note.
We like this rollout:
- Run shadow mode for 7–14 days.
- Compare predictions to what humans chose.
- Fix prompts, labels, and edge cases.
- Turn on limited actions, like tagging only.
- Add review gates before drafts become outbound messages.
Logging matters. Logs let you answer, “Why did the model tag this as billing?” without guessing.
Implementing NLP In A WordPress Stack
WordPress makes a good “home base” for NLP because it already holds your content, users, forms, and commerce data.
No-Code Options: Zapier, Make, n8n, Webhooks
If you do not want custom code, start with automation tools:
- Zapier: Quick to ship for common SaaS connectors.
- Make: Good for multi-step scenarios and data shaping.
- n8n: Good when you want more control or self-hosting.
- Webhooks: The glue between WordPress events and your NLP service.
No-code affects speed. It also affects auditability. We still document each step like an SOP so someone can maintain it six months later.
WordPress And WooCommerce Touchpoints: Hooks, Fields, And Queues
On the WordPress side, we often connect NLP to:
- Hooks like
save_postfor content drafts. - WooCommerce events for new products, refunds, and completed orders.
- Form plugins (Gravity Forms, WPForms) for lead intake.
- Custom fields (ACF) for storing extracted intent, category, or summary.
- Queues so jobs run reliably and do not slow page loads.
A queue affects site stability. Stability affects conversions. This is why we avoid “run the model on page load” setups.
If you are building from scratch, it helps to start with a site that is structured for growth. Our WordPress website development work usually includes the field model and workflow map upfront, so NLP has a clean place to write results.
Risks, Privacy, And Compliance Boundaries
NLP touches user text. User text often includes sensitive data. That is where teams get nervous, and they should.
The FTC has warned businesses to be careful with claims about what AI can do and to avoid misleading statements. That guidance applies when you publish AI-assisted content or sell AI features.
Data Minimization, Redaction, And Storage Policies
Set hard rules early:
- Collect only what you need. Less input reduces privacy exposure.
- Redact sensitive fields before sending text to a model.
- Set retention limits for logs and model inputs.
- Restrict who can view prompts and outputs.
Data handling affects risk. Risk affects whether you can scale the workflow past a pilot.
Disclosure, Accuracy Limits, And Regulated Content Review
If you work in legal, medical, finance, or insurance, keep humans in charge:
- A model can draft. A licensed professional must review.
- A model can summarize a document. A professional must confirm facts.
- A model should not invent citations or policies.
If you publish AI-assisted content, add an editorial checklist. If you message customers, add a review gate until error rates drop.
For privacy rules in the EU context, the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) has stressed principles like data minimization and purpose limitation under GDPR. Even if your business is US-based, those principles are useful when you serve EU customers.
How To Start: Low-Risk Pilots That Pay Off Quickly
We start small because small projects teach faster.
Choose One Queue, One Metric, And One Rollback Plan
Pick a single queue where text piles up:
- “New contact form leads”
- “Refund requests”
- “Shipping issue tickets”
- “New product drafts waiting for cleanup”
Then set one metric:
- Time to first response
- Tickets handled per agent per day
- Lead response time
- Editor time per post
Last, set a rollback plan:
- Turn off the automation without breaking the site.
- Keep manual processing as the fallback.
- Keep logs so you can learn even when you pause.
This is the part nobody wants to write down. It is also the part that keeps the pilot from becoming a scary science project.
Conclusion
Natural Language Processing (NLP) pays off when you treat it like a workflow tool, not a magic mind. Map the trigger and the output, keep the input small, log everything, and add human review where facts and compliance matter.
If you want a practical next step, pick one text-heavy queue on your WordPress site and run NLP in shadow mode for two weeks. You will learn more from that log than from ten more hours of tool shopping.
Sources
- Natural Language Processing (NLP), IBM, 2024, https://www.ibm.com/topics/natural-language-processing
- Machine Learning Crash Course: Feature Engineering, Google, 2023, https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/feature-engineering
- Artificial Intelligence and Algorithms: Guidance for Business, Federal Trade Commission, 2021, https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/blog/2021/04/aiming-truth-fairness-equity-your-companys-use-ai
- Guidelines 01/2020 on processing personal data in the context of connected vehicles and mobility related applications (data minimization principles apply broadly), European Data Protection Board (EDPB), 2020, https://www.edpb.europa.eu/our-work-tools/our-documents/guidelines/guidelines-012020-processing-personal-data_en
Frequently Asked Questions About Natural Language Processing (NLP)
What is Natural Language Processing (NLP) and what does it do on a website?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) helps software work with human language from emails, chats, reviews, and form entries. It can detect intent, extract key details, summarize long threads, and draft responses. On websites, NLP turns messy text into structured signals your team can route, review, and act on.
How does Natural Language Processing (NLP) help WordPress and WooCommerce support teams?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) can classify incoming tickets (billing vs shipping vs technical), extract order IDs and dates, and summarize long conversations into quick briefs. Many teams run NLP on every new ticket, then send agents a short summary and suggested reply so response time improves without auto-sending risky messages.
What are the most common NLP tasks businesses should start with?
The most common NLP tasks are classification, extraction, summarization, and generation. For most businesses, starting with classification and extraction is the fastest, lowest-risk win because outputs can be stored as tags or custom fields. Summaries and drafted text are useful too, but usually need tighter review guardrails.
What’s the best way to roll out Natural Language Processing (NLP) safely?
Use a simple workflow map: trigger, input, job, output, and guardrails. Start in “shadow mode” for 7–14 days so NLP only writes to logs or private notes. Compare results to human decisions, adjust prompts and labels, then enable limited actions like tagging before allowing any customer-facing drafts.
How is rules-based NLP different from machine learning and LLM-based NLP?
Rules-based NLP uses explicit patterns (for example, “if ‘refund’ appears, tag billing”) and is predictable but brittle. Machine learning classifiers learn from labeled examples and handle variation better. LLM-based NLP can summarize, extract, and draft in one step, but it’s more likely to drift and needs stronger constraints.
Can Natural Language Processing (NLP) handle sensitive customer data and stay compliant?
Yes, but only with deliberate privacy controls. Minimize what text you send, redact sensitive fields, set retention limits for logs, and restrict access to prompts and outputs. For regulated topics (legal, medical, finance), keep humans responsible for final decisions and avoid publishing AI-generated claims without an editorial review checklist.
Some of the links shared in this post are affiliate links. If you click on the link & make any purchase, we will receive an affiliate commission at no extra cost of you.
We improve our products and advertising by using Microsoft Clarity to see how you use our website. By using our site, you agree that we and Microsoft can collect and use this data. Our privacy policy has more details.